-
About NBK
-
Korea Biobank Project
-
Biobanking Activities
-
Access&Sharing
-
Resources
-
Contact Us
-
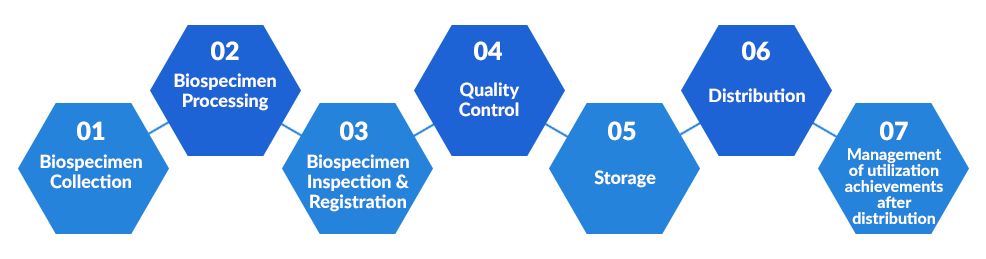
Biospecimen Collection
NBK collects blood and urine from participants through institutional projects (cohort projects, etc.) conducted by KNIH.
-
Processing
The collected human biospecimen are transported to a processing facility(contracted external company( e.g Seegene, GC labs, etc.)), where the blood is separated into serum, plasma, buffy coat, and so on, and DNA samples are produced
HuBIS_Tracker, a biobank information system, issues barcodes attached to biospecimen storage containers and storage box barcodes, and a reception file* is created. Barcodes are created using the biospecimen CODE (bCODE) system, a separate identifying code that anonymizes the donor's personal information.
* A file that records various information necessary for the storage and management of biospecimen (donor's basic information, human biospecimen type and quantity, quality control outcomes, etc.)
-
Inspection and Registration
The processed human biospecimen are transported to NBK using a transport ice box filled with dry ice, and the quantity of biospecimen, the adhesion status of the barcode label attached to the storage container, contamination and damage status of the storage container are inspected by comparing the transported biospecimen and the reception file.
If the inspection reveals no problem, the reception file is registered in the Biobank Information System (HuBIS_Sam), the location information of the biospecimen inside the transported storage box is inspected by HuBIS_Sam, and the specimen are stored in the freezer.
-
Quality Control
Quality control is performed according to the characteristics and types of biospecimen received. In addition to quality control using NBK – SOPs, measures such as total inspection are employed to check whether the location information stored in HuBIS_Sam matches the actual biospecimen and where a backup bank for distribution and storage of some of the collected specimen is prepared against emergency situations such as natural disasters. Thus, a reliable quality control system is in place for the biospecimen.
-
Storage
For long-term storage, the biospecimens are separated according to characteristics and types and stored in a mechanical freezer at -75℃ (DNA, urine) and a liquid nitrogen freezer at -150℃ (serum, plasma, cells) under optimal storage temperature in frozen condition.
-
Distribution
NBK distributes human biospecimen (DNA, serum, plasma, urine, etc.), genetic and epidemiological information to domestic researchers.
Distribution consultation is conducted through the distribution consultation call center (ARS 1661-9070) during the distribution application process, and the Human Biobank Information System_Desk (HuBIS_Desk), a distribution application portal, is in operation so that distribution applications can be conveniently processed online.
In addition, the distributions are subject to approval every month by the Access and Sharing Committee, consisting of experts in cohort research, clinical research, industry, distribution applications, and so on.
-
Monitoring of Achievements
In order to monitor successful journal publications and patents produced utilizing the distribution resources, we track such achievements on a regular basis by contacting the principal investigator who applied for the distribution or the organization that made the distribution request.
-
Collection through institutional projects
|
Large-scale human bioresources are collected through institutional projects conducted by governmental agencies such as the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES)* and the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES)**. Bioresources collected through these projects account for 76% of the total human bioresources collected—246,000 from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES) and 96,000 from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) (as of December 31, 2021) |
* Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES): A large-cohort study for the general population aged 40 to 69. Bioresources such as blood and urine were collected through health examination, and a health- and lifestyle-related survey was conducted
(click here for the website ).
** Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES): A nationwide survey under Article 16 of the National Health Promotion Act. The sampling units and household members were selected considering the national representativeness of the health and nutritional status through a sample design, and blood samples were collected from selected household members through health examination
(click here for the website ).
-
Collection through biospecimen deposit
NBK is a biological resources center under the Act on the Acquisition, Management and Utilization of Bio-Resources for Research, and human bioresources collected or produced through national R&D projects are deposited in the center.
Human bioresources are deposited in NBK after
research consent in Form 34 or
donation consent in Form 41
(see the annexure in Korean of the Enforcement Regulations of Bioethics and Safety Act) has been obtained.
The resources are distributed to researchers after the quality control and information anonymization processes.
* Bioresources exempted from the donor's written consent pursuant to Article 16, Paragraph 3, of the Bioethics and Safety Act are excluded.
-
Collection of epidemiological information and genetic information
Epidemiological information and genetic information on bioresources and biospecimen are collected through the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES) and the Korean Genome Analysis Project. The collected epidemiological information and genetic information are distributed to researchers after an anonymization process.
- Epidemiological information: Collected for 235,000 people through surveys; clinical study items are publicly distributed.
- Genetic information: Includes Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP), imputation, Copy Number Variation (CNV), exome sequence, and whole genome sequence, for 117,000 people. It is publicly distributed.
-
Quality control by type of biospecimen

|
Quality control is conducted according to the characteristics and types of biospecimen.
|
NBK - Standard Operating Procedures(in Korea)![]()
-
Research on quality control methods of human body fluids
Serum and plasma have been publicly distributed since 2017, and with rapidly increasing demand of distribution, quality control research is under way to develop more objective quality control procedures in addition to the existing methods of SPREC record management and visual inspection.
- ▪ Serum: Examination of serum index (HIL index; Hemolysis, Icterus, Lipemia index), test strip method (EDTA, Glucose), colorimetric assay (Calcium, Glucose)
- ▪ Plasma: test strip method(EDTA, Glucose), colorimetric assay(Calcium, Glucose)
-
Total inspection of biospecimen
HuBIS_Sam and information on stored biospecimen are continuously matched, and inconsistencies in storage location, present status of specimen, and so on, are corrected.
-
Authentification of Biospecimen Identity
In the process of collecting and managing human bioresources in large quantities, errors in recording human bioresource information, cross-contamination, and barcode labeling often occur. These types of inconsistent information are corrected through Short Tandem Repeat (STR) and SNP analysis.
-
Operation of KBN - Backup Biobanks
KBN - Backup Biobank * is designated for separate and distributed storage of some of the collected
resources for safety of the collected bioresources in the event of emergencies such as natural disasters. NBK
provides technology, training, equipment, and cost support for the operation of backup bank, and conducts
regular check-up and inspection to ensure that bank operations and resource management are properly
performed.
* Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital was designated as a backup biobank considering the geographic conditions and facilities available.
-
Annual Proficiency Test
Annual proficiency testing program for human biospecimens has been in operation since 2013 to enhance the accuracy and precision of quality control of human bioresources collected and stored in domestic biobanks, and to standardize the quality control process.
The proficiency testing program of NBK is open to KBN biobanks, non-KBN biobanks, and other biobanking service providers. The testing is conducted on six items (DNA quantification and purity measurement, DNA microbial contamination test, RNA stability test, cell viability measurement, DNA extraction, and RNA extraction).

|
NBK operates the self-developed Human Biobank Informatics System (HuBIS), which manages the storage and dissemination of information on biological samples. HuBIS handles various biobank inventory data obtained from a central biobank, the 10 Hub biobanks, 25 cooperative biobanks, and 2 innovative consortium, which comprise the Korea Biobank Network (KBN). In addition, HuBIS is deployed, installed, and supported free of charge upon request even in non-KBN biobanks. The system is currently utilized by 65 biobanks. |
The Human Biobank Informatics System (HuBIS) is composed of three sub-programs divided by function, and each program runs a help desk on a regular basis and upgrades its function every year through maintenance projects to facilitate convenient use and efficient work by users.
[HuBIS Unit System]
| Unit System Name | Key Functions | Users | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| HuBIS_Sam | History management for the entire process of biospecimen collection, storage, and distribution | Biobank resources manager and information manager | In use by 65 domestic biobanks including KBN |
| HuBIS_Tracker | Bar code label issuance, cohort site management | Biospecimen depositor | In use by 29 domestic depository institutions |
| HuBIS_Desk |
Searching human bioresources for distribution,
Online consultation, Distribution application and review, human bioresources utilization and management |
Researcher,
Biobank distribution manager, Distribution board member |
In use by over 2,900 researchers using distribution service in Korea |
[Biobanks in use of HuBIS_Sam]
|
KBN
(36 Biobanks) |







|







|
|







|
|







|
|







|
|

|
|
|
Non-KBN
(28 Biobanks) |






|







|
|







|
|






|

|
The biospecimen storage space of NBK consists of two floors (3,203㎡) where up to 187 mechanical (792ℓ/unit, -73℃ to -77℃) and 474 liquid nitrogen (700ℓ/unit, -150℃ to -196℃) freezers can be installed. Currently, 187 mechanical freezers and 391 liquid nitrogen freezers are in operation (as of Jan 22), of which 10% are spare storage equipments , to which biospecimens are transferred in case of a failure in the existing storage equipment so that the biospecimen is maintained in a frozen state throughout. |
For stable and reliable management of a large quantity of storage facilities, routine inspection is carried out on a daily basis, and emergency generators and uninterruptible power supply (UPS) are provided for emergencies, so that in the event of power outage, power can be supplied to storage equipment for more than one week.
[Current Status of the biospecimen storage facilities]
| Liquid nitrogen freezer | Automated (semi-auto) liquid nitrogen freezer | Mechanical freezer | |
|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|
|
|
- Stored Biospecimen: Serum, Plasma, Cells
- Storage Temperature: -150℃~-196℃ - Number of Available Devices: 474 |
- Stored Biospecimen: Serum
- Storage Temperature: -150℃~-196℃ - Number of Available Devices: 5 |
- Stored Biospecimen: DNA, Urine
- Storage Temperature: -73℃~-77℃ - Number of Available Devices: 187 |
|
| Automated Storage Sample and Retrieval System (A) |
Automated Storage Sample and Retrieval System (B) |
Automated Storage Sample and Retrieval System (C) |
Automated Storage Sample and Retrieval System (D) |

|

|

|

|
|
- Stored Biospecimen: DNA
- Storage Temperature: -20℃ - Number of Available Devices: 1 |
- Stored Biospecimen: DNA
- Storage Temperature : -20℃ - Number of Available Devices: 2 |
- Stored Biospecimen: Serum, Plasma
- Storage Temperature: -80℃ - Number of Available Devices: 3 |
- Stored Biospecimen: Serum, Plasma
- Storage Temperature: -80℃ - Number of Available Devices: 3 |



